Mazda CX-5 SKYACTIV Engine
As societal responsibility forces automakers to pursue greater environmental performance, it tends push automakers to give less consideration to the driving pleasure and performance, something that drivers have always desired.
In the case of Mazda, it is determined not to let cars become simple transportation devices that offer nothing more. Driving is about the pleasant surprise and exhilaration of pressing the accelerator pedal for the first time, of having the car respond the driver’s every will as a sense of oneness forms between driver and car.
It’s also about the pride a car owner feels in knowing they are contributing to environmental conservation, and about the reliability that allows passengers to sit back and enjoy the drive while feel reassured about their safety and comfort. This is behind the development of SKYACTIV TECHNOLOGY as a technology that leads in delivering the excitement, exhilaration and pleasure of driving a car.
Hybrid technologies are garnering attention as one way to improve environmental performance, and Mazda is proceeding with plans to introduce its own version in the near future. Still, Mazda’s approach is not to simply adopt a hybrid system. Rather, it intends to fully leverage the advantages of reduced weight and improved efficiency achieved by SKYACTIV TECHNOLOGY. Reducing the size and weight of critical components, including the electric motors in this way will allow Mazda to create an ultra-efficient vehicle as the next generation. Hybrid vehicles that benefit from thorough efforts to evolve systems based on the internal combustion engine will better deliver the signature driving pleasure that embodies Mazda’s unique Zoom-Zoom driving experience. This is also true of the electric and hydrogen powered vehicles that are also in the works.
One distinctive characteristic of SKYACTIV TECHNOLOGY is that it foregoes the conventional method of developing each component and assembly individually. Instead, the entire car is reviewed at the beginning and then the most efficient system established for bringing it to production. It is a system that resolves what was previously thought to be conflicting issues. That is, the establishment of a flexible production concept that facilitates the ‘commonization’ of parts, assembly lines and also common architectures with a priority on achieving production efficiency, while at the same time realizing the ‘diversification’ necessary to satisfy the varying needs of customers. Mazda call this system ‘Monotsukuri’, which means “the entire process of making things” in Japanese
When developing the SKYACTIV engine, Mazda laid out certain objectives designed to bring car, driver and passengers closer, and the following section introduces the feelings it wishes wish to convey to customers.
1) When starting the engine
It should respond the instant the accelerator pedal is pressed; and when idling, there should be an absence of disturbing vibration to lend the feeling of a precision machine in operation. The driver and passengers are to be instilled with the anticipation of a pleasant drive. One might even say that the sound of the engine is like pleasing background music that sets the scene.
The features that contribute to the above are direct injection, and the reduction of friction in the moving parts.
2) When merging with traffic on the highway
It is quite a common practice for drivers to press the accelerator pedal, confirm the position of cars following and then ease off the pedal again. With SKYACTIV TECHNOLOGY, acceleration is smooth when you do press the pedal again. This is done by dialling in a linear and direct acceleration feel through the throttle input system.
3) When driving at highway speeds
SKYACTIV TECHNOLOGY relieves you of the stress and fatigue of driving on the highway or when taking long trips. This is one of the appealing features of the technology. There is the distinguishable lack of the need to work the accelerator pedal to achieve a desired speed. Also, you can confirm the benefit of outstanding fuel economy even as you drive, through a stable and smooth driving performance, and quietness that does not cause the driver stress or fatigue
Technology of the SKYACTIV-G Engine
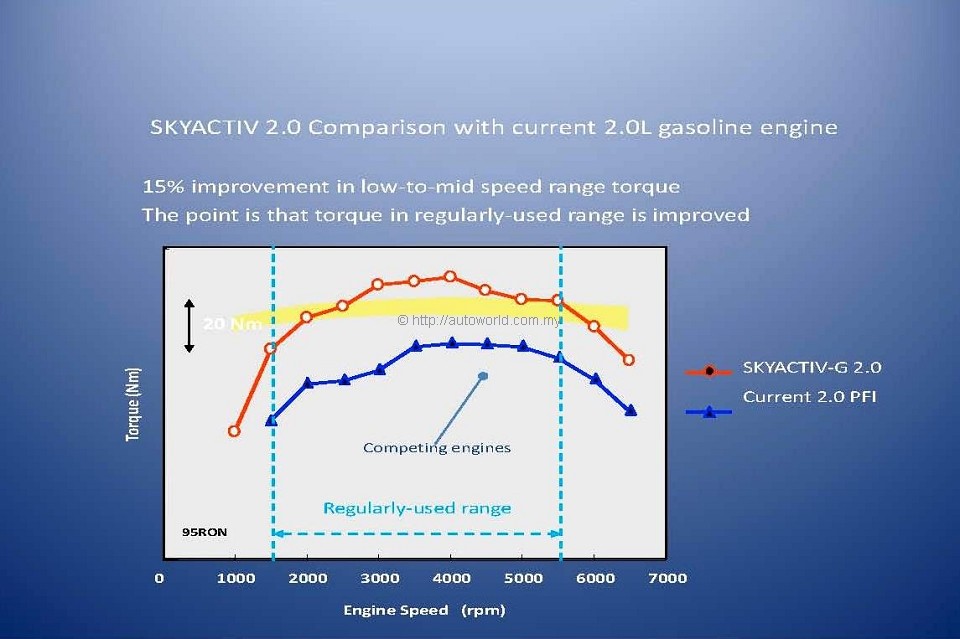
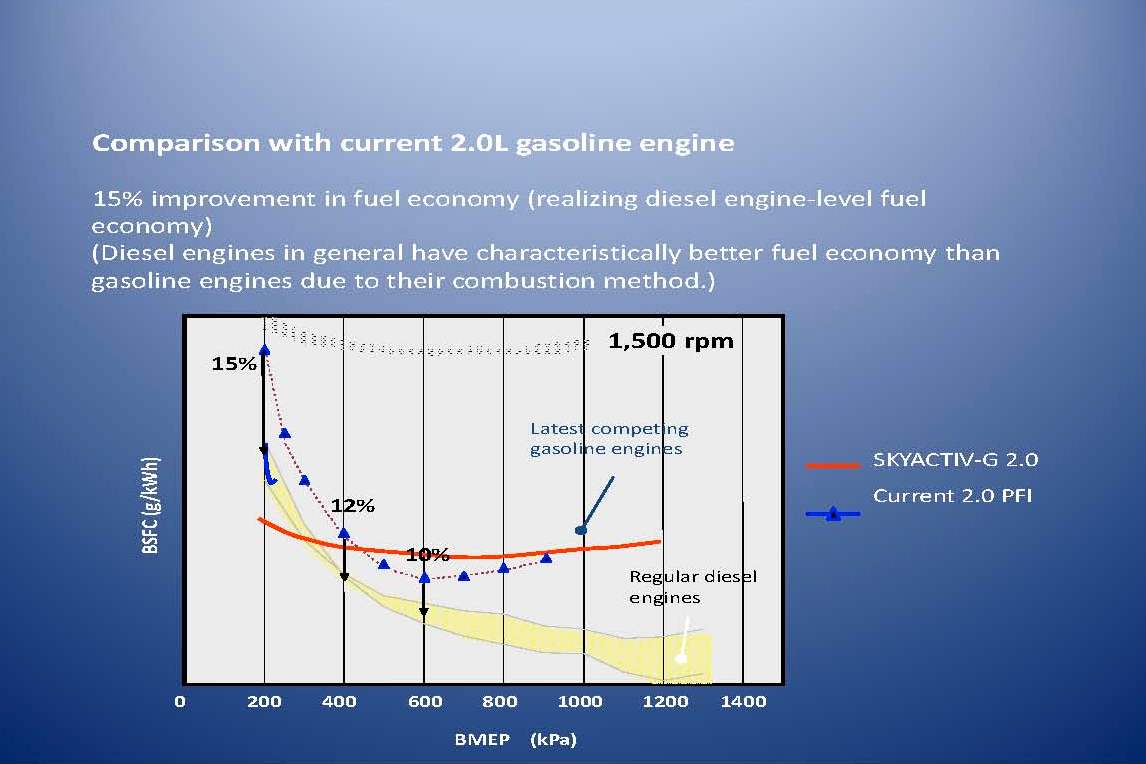
The SKYACYIV G (Gasoline) engine is the new generation high-efficiency direct-injection engine, which achieves the world’s highest compression ratio (14:1) and improves fuel economy and low- to mid-range torque by 15%. (In Malaysia, the compression ratio is reduced to 13:1 to cater for the lower grade of petrol available.
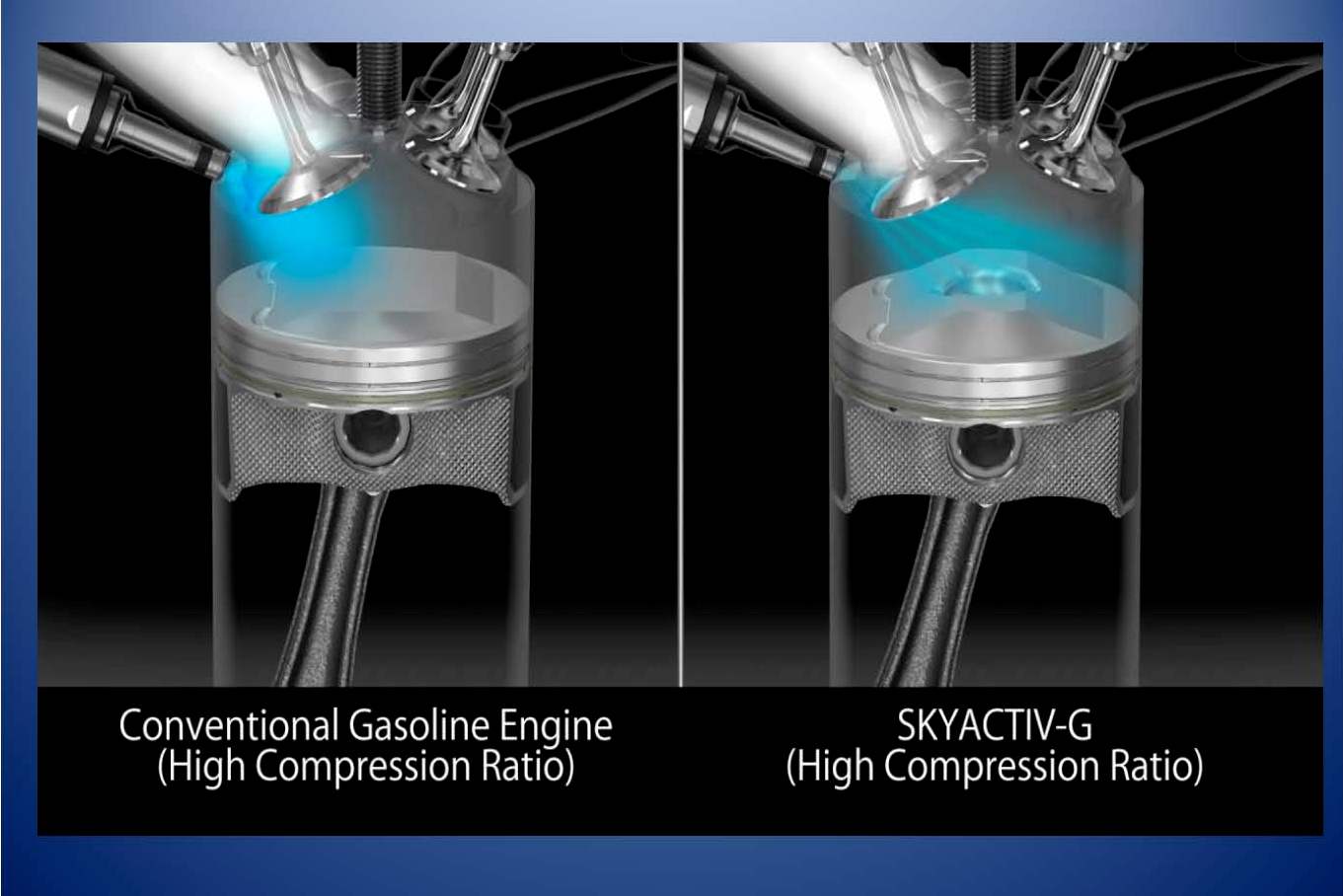
The key control factor with SKYACTIV is the compression ratio. With conventional gasoline engines, the compression ratio on direct injection engines and high performance engines has been increasing in recent years, however, the compression ratio of general gasoline engines is 9 to 11, and it is around 12.5 even on high performance engines for sports cars which require premium gasoline.
SKYACTIV-G has a world-top compression ratio of 13 to 14. Fuel quality affects the compression ratio, but even for the markets where the fuel quality is comparatively low, the SKYACTIV-G realizes a world-top compression ratio of 13 to 14 which is higher than that of the high performance engines used on sports cars and equal to the engines used on race cars.
As a result of this break-through, the SKYACTIV-G provides a 15 percent improvement in low speed torque (the 2.0 litre SKYACTIV-G compared to the Mazda conventional 2.0 litre engine). The customer benefit is that the torque used in day to day driving applications has improved.
A 15 percent improvement in fuel economy brings the SKYACTIV-G on par with a diesel engine of the same capacity. Environmentally, there is also a 15 percent reduction in CO2 emissions, and the engine can run on RON 95 fuel.
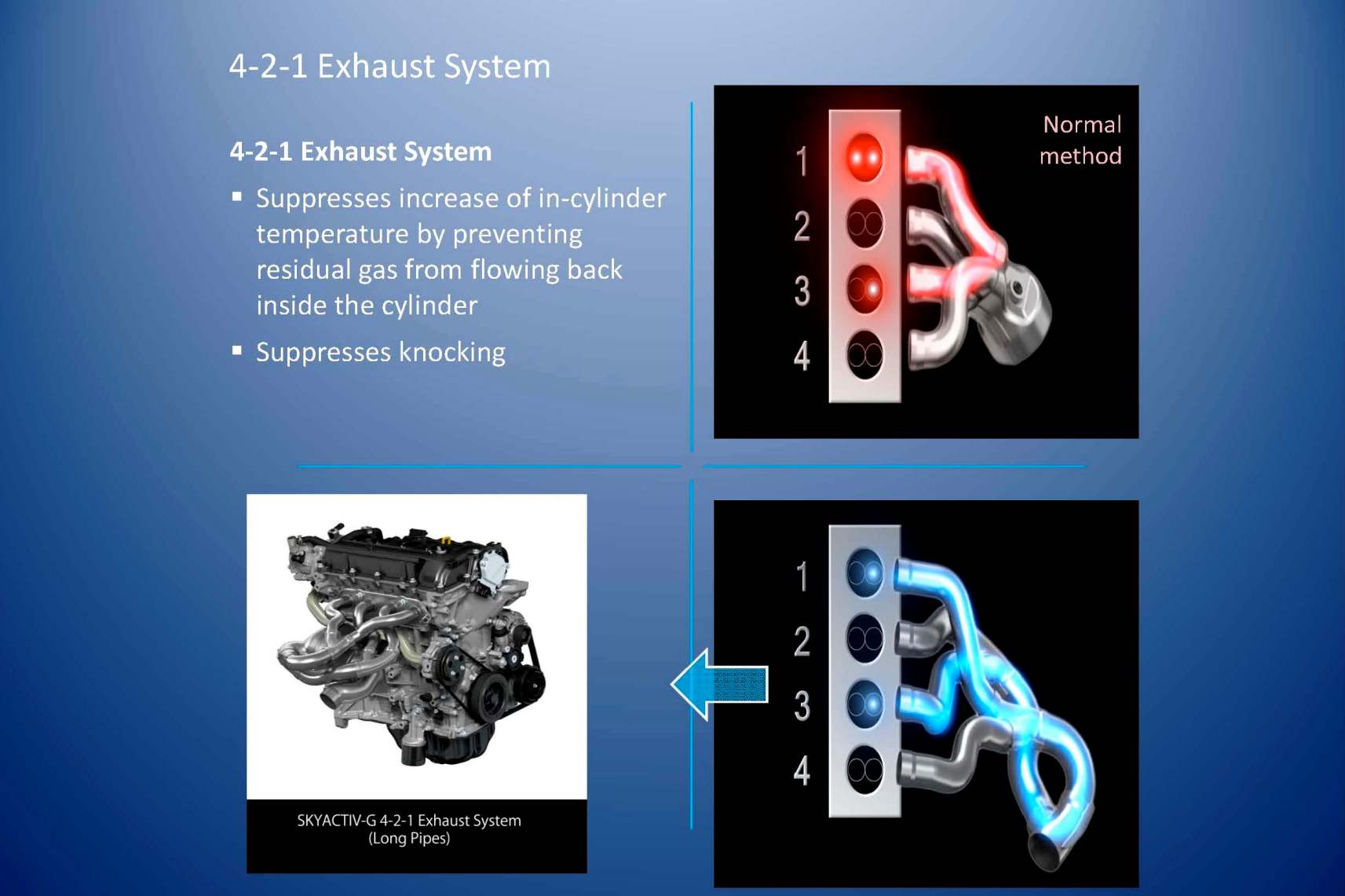
In order to prevent ‘knocking’, the Mazda SKYACTIV-G adopted a newly developed 4-2-1 exhaust system, which incidentally is similar to those used in race cars. Knocking can be prevented if the amount of residual gas in the combustion chamber is reduced. The SKYACTIV-G 4-2-1 exhaust system with long pipes in the exhaust manifold reduces the amount of residual gas in the exhaust manifold.
Adopting a piston cavity on the piston crown and optimizing fuel injection in order to formulate a stratified air-fuel mixture around the spark plug realizes stable combustion at all times. The piston cavity also resolves the issue of the initial flame coming in contact with the piston head and generating a cooling loss.
In designing the engine, Mazda aimed to thoroughly reduce inertial weight and mechanical resistance. By reducing weight by 10 percent and reducing mechanical resistance by 30 percent, the result is smoother action and improved responsiveness of its respective parts.
SKYACTIV-G satisfies the strict Euro Stage 5 emissions standards.